Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
White chocolate Smarties - Nestlé
White chocolate Smarties - Nestlé
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 7613287912510 (EAN / EAN-13)
Packaging: fr:boîte : recycler
Brands: Nestlé
Categories: Snacks, Sweet snacks, Cocoa and its products, Confectioneries, Chocolate candies, Bonbons, Chocolates, White chocolates
Labels, certifications, awards:
FSC, FSC Recycling, Rainforest Alliance, Rainforest Alliance Cocoa

Origin of ingredients: Belgium
Countries where sold: Ireland
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
35 ingredients
Sugar, Skimmed milk powder, Cocoa butter, Wheat flour, Butterfat (from Milk), Whey powder product (from Milk), Rice starch, Emulsifier (Lecithins), Potato starch, Colours (Beetroot red, Beta-carotene, Curcumin), Spirulina concentrate, Glazing agents (Carnauba wax, Beeswax white), Fruit and vegetable concentrates (Safflower, Radish), Barley malt extract, Acids (Citric acid, Acetic acid), Acidity regulator (Trisodium citrate), Natural flavouring. IMPORTANT: YOUNG CHILDREN (LESS THAN 4 YEARS) HAVE LIMITED CHEWING ABILITY AND COULD CHOKE ON SMALL SWEETS. Rainforest Alliance Certified cocoa. Find out more at ra.org NUTRITIONAL COMPASSAllergens: Gluten, Milk
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E100 - Curcumin
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Additive: E162 - Beetroot red
- Additive: E322 - Lecithins
- Additive: E903 - Carnauba wax
- Ingredient: Colour
- Ingredient: Emulsifier
- Ingredient: Flavouring
- Ingredient: Glazing agent
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160ai - Beta-carotene
Beta-Carotene: β-Carotene is an organic, strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits. It is a member of the carotenes, which are terpenoids -isoprenoids-, synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units and thus having 40 carbons. Among the carotenes, β-carotene is distinguished by having beta-rings at both ends of the molecule. β-Carotene is biosynthesized from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.β-Carotene is the most common form of carotene in plants. When used as a food coloring, it has the E number E160a. The structure was deduced by Karrer et al. in 1930. In nature, β-carotene is a precursor -inactive form- to vitamin A via the action of beta-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase.Isolation of β-carotene from fruits abundant in carotenoids is commonly done using column chromatography. It can also be extracted from the beta-carotene rich algae, Dunaliella salina. The separation of β-carotene from the mixture of other carotenoids is based on the polarity of a compound. β-Carotene is a non-polar compound, so it is separated with a non-polar solvent such as hexane. Being highly conjugated, it is deeply colored, and as a hydrocarbon lacking functional groups, it is very lipophilic.Source: Wikipedia
-
E162 - Beetroot red
Betanin: Betanin, or Beetroot Red, is a red glycosidic food dye obtained from beets; its aglycone, obtained by hydrolyzing away the glucose molecule, is betanidin. As a food additive, its E number is E162. The color of betanin depends on pH; between four and five it is bright bluish-red, becoming blue-violet as the pH increases. Once the pH reaches alkaline levels betanin degrades by hydrolysis, resulting in a yellow-brown color. Betanin is a betalain pigment, together with isobetanin, probetanin, and neobetanin. Other pigments contained in beet are indicaxanthin and vulgaxanthins.Source: Wikipedia
-
E260 - Acetic acid
Acetic acid: Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is a colorless liquid organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH -also written as CH3CO2H or C2H4O2-. When undiluted, it is sometimes called glacial acetic acid. Vinegar is no less than 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Acetic acid has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell. In addition to household vinegar, it is mainly produced as a precursor to polyvinyl acetate and cellulose acetate. It is classified as a weak acid since it only partially dissociates in solution, but concentrated acetic acid is corrosive and can attack the skin. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid -after formic acid-. It consists of a methyl group attached to a carboxyl group. It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for acetic acid is about 6.5 million metric tons per year -Mt/a-, of which approximately 1.5 Mt/a is met by recycling; the remainder is manufactured from methanol. Vinegar is mostly dilute acetic acid, often produced by fermentation and subsequent oxidation of ethanol.Source: Wikipedia
-
E322 - Lecithins
Lecithins are natural compounds commonly used in the food industry as emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Extracted from sources like soybeans and eggs, lecithins consist of phospholipids that enhance the mixing of oil and water, ensuring smooth textures in various products like chocolates, dressings, and baked goods.
They do not present any known health risks.
-
E330 - Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits such as lemons, oranges, and limes.
It is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, acidulant, and preservative due to its tart and refreshing taste.
Citric acid is safe for consumption when used in moderation and is considered a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive by regulatory agencies worldwide.
-
E331 - Sodium citrates
Sodium citrate: Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citrate -though most commonly the third-: Monosodium citrate Disodium citrate Trisodium citrateThe three forms of the salt are collectively known by the E number E331. Sodium citrates are used as acidity regulators in food and drinks, and also as emulsifiers for oils. They enable cheeses to melt without becoming greasy.Source: Wikipedia
-
E331iii - Trisodium citrate
Sodium citrate: Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citrate -though most commonly the third-: Monosodium citrate Disodium citrate Trisodium citrateThe three forms of the salt are collectively known by the E number E331. Sodium citrates are used as acidity regulators in food and drinks, and also as emulsifiers for oils. They enable cheeses to melt without becoming greasy.Source: Wikipedia
-
E903 - Carnauba wax
Carnauba wax: Carnauba -; Portuguese: carnaúba [kaʁnɐˈubɐ]-, also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the palm Copernicia prunifera -Synonym: Copernicia cerifera-, a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Piauí, Ceará, Maranhão, Bahia, and Rio Grande do Norte. It is known as "queen of waxes" and in its pure state, usually comes in the form of hard yellow-brown flakes. It is obtained from the leaves of the carnauba palm by collecting and drying them, beating them to loosen the wax, then refining and bleaching the wax.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
May contain palm oil
Ingredients that may contain palm oil: E160ai
-
Non-vegan
Non-vegan ingredients: Skimmed milk powder, Butterfat, Milk, MilkSome ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Vegetarian status unknown
Unrecognized ingredients: Whey-powder-product, Beeswax-white, Important, Young-children, Less-than-4-years, Have-limited-chewing-ability-and-could-choke-on-small-sweets, Find-out-more-at-ra-org-nutritional-compassSome ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
We need your help!
Some ingredients could not be recognized.
We need your help!
You can help us recognize more ingredients and better analyze the list of ingredients for this product and others:
- Edit this product page to correct spelling mistakes in the ingredients list, and/or to remove ingredients in other languages and sentences that are not related to the ingredients.
- Add new entries, synonyms or translations to our multilingual lists of ingredients, ingredient processing methods, and labels.
If you would like to help, join the #ingredients channel on our Slack discussion space and/or learn about ingredients analysis on our wiki. Thank you!
: Sugar, Skimmed milk powder, Cocoa butter, Wheat flour, Butterfat (from Milk), Whey powder product (from Milk), Rice starch, Emulsifier (Lecithins), Potato starch, Colours (Beetroot red, Beta-carotene, Curcumin), Spirulina concentrate, Glazing agents (Carnauba wax, Beeswax white), Fruit and vegetable concentrates (Safflower, Radish), Barley malt extract, Acids (Citric acid, Acetic acid), Acidity regulator (Trisodium citrate), Natural flavouring, IMPORTANT (YOUNG CHILDREN (LESS THAN 4 YEARS), HAVE LIMITED CHEWING ABILITY and COULD CHOKE ON SMALL SWEETS, Find out more at ra.org NUTRITIONAL COMPASS)- Sugar -> en:sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 5.55555555555556 - percent_max: 100
- Skimmed milk powder -> en:skimmed-milk-powder - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 19054 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 50
- Cocoa butter -> en:cocoa-butter - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 16030 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 33.3333333333333
- Wheat flour -> en:wheat-flour - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9410 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 25
- Butterfat -> en:butterfat - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - from_palm_oil: maybe - ciqual_food_code: 16401 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- from Milk -> en:milk - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 19051 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- Whey powder product -> en:whey-powder-product - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 16.6666666666667
- from Milk -> en:milk - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 19051 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 16.6666666666667
- Rice starch -> en:rice-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 14.2857142857143
- Emulsifier -> en:emulsifier - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 12.5
- Lecithins -> en:e322 - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 12.5
- Potato starch -> en:potato-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 11.1111111111111
- Colours -> en:colour - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- Beetroot red -> en:e162 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 10
- Beta-carotene -> en:e160ai - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- Curcumin -> en:e100 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.33333333333333
- Spirulina concentrate -> en:spirulina-concentrate - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 20984 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 9.09090909090909
- Glazing agents -> en:glazing-agent - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 8.33333333333333
- Carnauba wax -> en:e903 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 8.33333333333333
- Beeswax white -> en:beeswax-white - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.16666666666667
- Fruit and vegetable concentrates -> en:fruit-and-vegetable-concentrates - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 7.69230769230769
- Safflower -> en:safflower - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 7.69230769230769
- Radish -> en:radish - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 20045 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.84615384615385
- Barley malt extract -> en:barley-malt-extract - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 7.14285714285714
- Acids -> en:acid - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 6.66666666666667
- Citric acid -> en:e330 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 6.66666666666667
- Acetic acid -> en:e260 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 3.33333333333333
- Acidity regulator -> en:acidity-regulator - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 6.25
- Trisodium citrate -> en:e331iii - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 6.25
- Natural flavouring -> en:natural-flavouring - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- IMPORTANT -> en:important - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- YOUNG CHILDREN -> en:young-children - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- LESS THAN 4 YEARS -> en:less-than-4-years - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- HAVE LIMITED CHEWING ABILITY and COULD CHOKE ON SMALL SWEETS -> en:have-limited-chewing-ability-and-could-choke-on-small-sweets - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.5
- Find out more at ra.org NUTRITIONAL COMPASS -> en:find-out-more-at-ra-org-nutritional-compass - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.66666666666667
- YOUNG CHILDREN -> en:young-children - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
Nutrition
-
Bad nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 0This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 0
- Proteins: 4 / 5 (value: 7.2, rounded value: 7.2)
- Fiber: 0 / 5 (value: 0.2, rounded value: 0.2)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 0.0576443142361072, rounded value: 0.1)
Negative points: 27
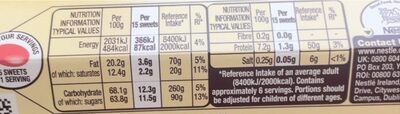
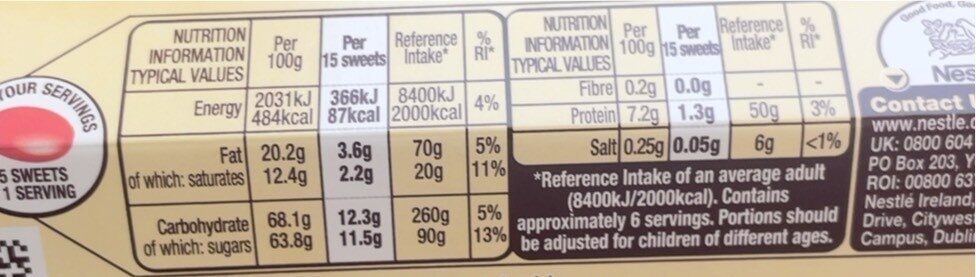
- Energy: 6 / 10 (value: 2025, rounded value: 2025)
- Sugars: 10 / 10 (value: 63.8, rounded value: 63.8)
- Saturated fat: 10 / 10 (value: 12.4, rounded value: 12.4)
- Sodium: 1 / 10 (value: 100, rounded value: 100)
The points for proteins are not counted because the negative points are greater or equal to 11.
Nutritional score: (27 - 0)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in high quantity (20.2%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in high quantity (12.4%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in high quantity (63.8%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in low quantity (0.25%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlCompared to: White chocolates Energy 2,025 kj
(484 kcal)-9% Fat 20.2 g -34% Saturated fat 12.4 g -31% Carbohydrates 68.1 g +23% Sugars 63.8 g +24% Fiber 0.2 g Proteins 7.2 g +15% Salt 0.25 g -7% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 0.058 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score C - Moderate environmental impact
The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: D (Score: 39/100)
Category: White chocolate bar
Category: White chocolate bar
- PEF environmental score: 0.76 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 11.32 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
58.5 %Processing
35.4 %Packaging
1.4 %Transportation
4.1 %Distribution
0.6 %Consumption
0.0 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Bonus: +10
Environmental policy: +2
Transportation: +8
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact Belgium 100 %Medium
-
Packaging with a low impact
Malus: -1
Shape Material Recycling Impact 1 Box Cardboard Recycle with drink cartons Low
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: C (Score: 58/100)
Product: White chocolate Smarties - Nestlé
Life cycle analysis score: 39
Sum of bonuses and maluses: +19
Final score: 58/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 5.9 km in a petrol car
1132 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: White chocolate bar (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
46.4 %Processing
49.6 %Packaging
0.9 %Transportation
2.9 %Distribution
0.2 %Consumption
0.0 %
Packaging
-
Packaging with a low impact
-
Packaging parts
1 x Box (Cardboard)
-
Packaging materials
Material % Packaging weight Paper or cardboard
-
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Origins of ingredients with a medium impact
Origin of the product and/or its ingredients % of ingredients Impact Belgium 100 %Medium
Labels
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by kiliweb
Last edit of product page on by william-declercq.
Product page also edited by averment, openfoodfacts-contributors, roboto-app, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlk1Lb_aHmW_-MCbvvhPXm_LVDLfIU-4u2LSkHKo, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvlnVdCOXPpwmUJhzQpnWh6_3WcYHzQeAo8NbHK6s.